Medical Term for Bones Continue to Grown Childhood
-
Bone disorders can be caused by injury, infection, or cancer, be inherited, occur as part of a child's growth, or occur for no known reason.
-
Some bone disorders can cause pain and difficulty walking, whereas others cause no symptoms.
-
Doctors base the diagnosis on a thorough history, close observation and examination, and the selective use of x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
-
Treatment depends on the disorder.
Children's bones grow continually and reshape (remodel) themselves extensively. Growth proceeds from a vulnerable part of the bone called the growth plate. In remodeling Bones  , old bone tissue is gradually replaced by new bone tissue. Many bone disorders come from the changes that occur in a growing child's musculoskeletal system. These disorders may get better or worsen as the child grows. Other bone disorders may be inherited or occur in childhood for no known reason.
, old bone tissue is gradually replaced by new bone tissue. Many bone disorders come from the changes that occur in a growing child's musculoskeletal system. These disorders may get better or worsen as the child grows. Other bone disorders may be inherited or occur in childhood for no known reason.
People think of bones as solid objects. But bones need to grow along with the rest of the child's body. Children's bones grow from soft areas of cartilage near the ends of bones. These areas are called growth plates. When children have finished growing, growth plates become solid bone. After growth plates become solid, bones do not grow in length. That is why people do not become taller after a certain point in late adolescence. Although bones repair themselves, such as after an injury, that repair does not involve the growth plates.
Locating Growth Plates
Growth plates (indicated by the pink lines) are areas of cartilage near the ends of long bones, such as the arm and leg bones. They enable bones to lengthen until children reach their full height.
Bone disorders in children can result from causes that affect people of all ages, including injury, infection (osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis is a bone infection usually caused by bacteria, mycobacteria, or fungi. Bacteria, mycobacteria, or fungi can infect bones by spreading through the bloodstream or, more often, by... read more ), or cancer. Causes of bone disorders that affect mainly children typically involve the gradual misalignment of bones, which is caused by forces exerted on the growth plates as children are developing. A poor blood supply can also damage the growth plate, as can separation from the rest of the bone or even minor misalignment. Damage to the growth plate suppresses the growth of bones, distorts the joint, and can cause long-lasting joint damage (arthritis).
Certain rare connective tissue disorders Overview of Connective Tissue Disorders in Children Connective tissue is the tough, often fibrous tissue that binds the body's structures together and provides support and elasticity. Muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons are built... read more can also affect the bones. They include Marfan syndrome Marfan Syndrome Marfan syndrome is a rare hereditary disorder of connective tissue, resulting in abnormalities of the eyes, bones, heart, blood vessels, lungs, and central nervous system. This syndrome is caused... read more 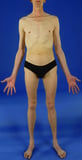 , osteogenesis imperfecta Osteogenesis Imperfecta Osteogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary disorder that disrupts the proper formation of bones and makes bones abnormally fragile. Typical symptoms include weak bones that break easily. The diagnosis... read more
, osteogenesis imperfecta Osteogenesis Imperfecta Osteogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary disorder that disrupts the proper formation of bones and makes bones abnormally fragile. Typical symptoms include weak bones that break easily. The diagnosis... read more 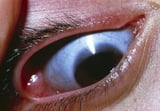 , and osteochondrodysplasias Osteochondrodysplasias Osteochondrodysplasias are a group of rare hereditary disorders of connective tissue, bone, or cartilage that cause the skeleton to develop abnormally. In osteochondrodysplasias, the growth... read more . Osteopetroses Osteopetroses Osteopetroses are a group of rare hereditary disorders that increase the density of bones and cause bones to grow abnormally. These disorders occur when the body does not recycle old bone cells... read more are other rare hereditary disorders that increase the density of bones, cause bones to grow abnormally, or both.
, and osteochondrodysplasias Osteochondrodysplasias Osteochondrodysplasias are a group of rare hereditary disorders of connective tissue, bone, or cartilage that cause the skeleton to develop abnormally. In osteochondrodysplasias, the growth... read more . Osteopetroses Osteopetroses Osteopetroses are a group of rare hereditary disorders that increase the density of bones and cause bones to grow abnormally. These disorders occur when the body does not recycle old bone cells... read more are other rare hereditary disorders that increase the density of bones, cause bones to grow abnormally, or both.
Bone disorders sometimes cause painless deformities. Some deformities may affect a child's ability to walk or use the limbs.
-
A doctor's evaluation
-
X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and laboratory tests
-
Depends on the disorder
Treatment of bone disorders varies depending on the condition. Children may outgrow some disorders. However, others may require bracing or surgical intervention.
If the growth plate becomes damaged, surgery may help. Accurately realigning separated or misaligned ends of the growth plate may surgically restore normal bone growth. By decreasing the irritation caused by misalignment, surgery may prevent the development of arthritis in the joint.
CLICK HERE FOR THE PROFESSIONAL VERSION

Copyright © 2022 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/children-s-health-issues/bone-disorders-in-children/overview-of-bone-disorders-in-children
0 Response to "Medical Term for Bones Continue to Grown Childhood"
Post a Comment